What is an EGR valve and how does it work?
What is an EGR?
Integral to the vehicle’s engine management system, the aptly named exhaust gas recirculation valve, or EGR valve for short, recirculates finely metered quantities of exhaust gas to the engine intake system for increased engine efficiency, reduced fuel consumption and lower NOx emissions.
Within modern internal combustion engines, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) is a method to control Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) emissions, produced as a by-product during the combustion process.
Air from the environment, mostly a combination of Oxygen and Nitrogen, combines with fuel and ignites inside the combustion chamber, temperatures increase and produce NOx emissions.
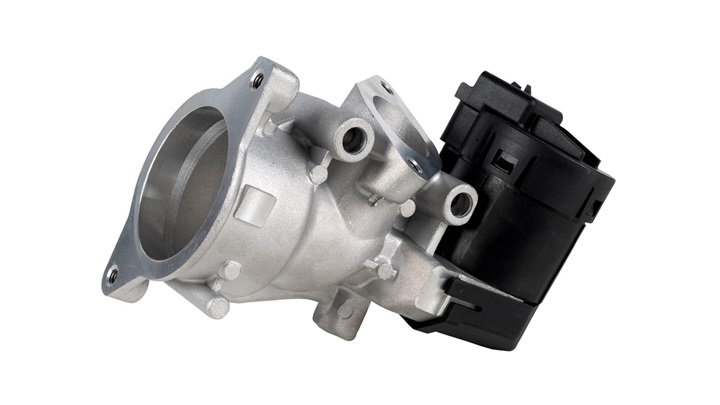

How does it work?
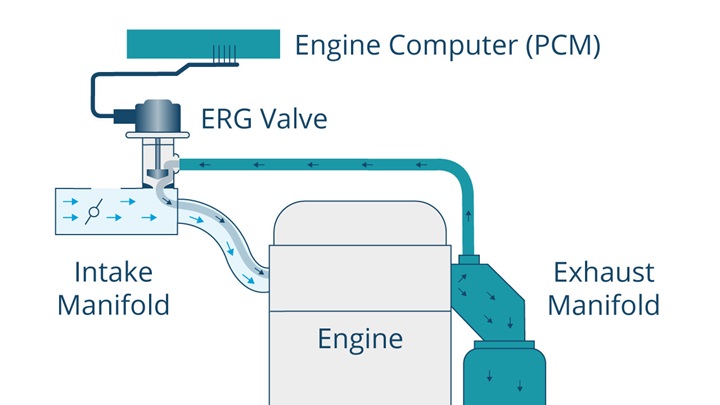
The EGR system works by returning a small portion of exhaust gas to the engine’s combustion chambers through the intake manifold, lowering combustion temperatures and therefore reducing the amount of NOx emitted.
The EGR valve is the main component of the EGR system and it’s normally closed. It connects the exhaust manifold to the intake manifold and is controlled by either a vacuum or a built-in electric step motor. The function of the EGR valve is to control the flow of exhaust gas being recirculated depending on the engine load.
The majority of modern vehicles incorporate EGR valves into their design to reduce NOx emissions and therefore meet stringent emissions regulations. EGR systems recycle a portion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber, where it combines with fresh intake air.
This lowers the amount of Oxygen and increases the water vapour content to the combustion mixture which reduces the peak combustion temperature. Because more NOx is created as peak combustion temperature rises, the EGR valve effectively reduces the amount of NOx produced by the engine.
The EGR valve begins working once the engine has started, attained the correct operating temperature and the vehicle’s speed increases. Gradually, the EGR valve regulates the flow of exhaust gases.
Once the vehicle slows down and the engine stops, the EGR valve will return to its closed position and prevent the flow of exhaust gases.